Mapping the Final Glacial Most: A Journey into the Frozen Previous
Associated Articles: Mapping the Final Glacial Most: A Journey into the Frozen Previous
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate via the intriguing subject associated to Mapping the Final Glacial Most: A Journey into the Frozen Previous. Let’s weave attention-grabbing data and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mapping the Final Glacial Most: A Journey into the Frozen Previous

The Final Glacial Most (LGM), the height of the final ice age roughly 20,000 years in the past, dramatically reshaped the Earth’s panorama and profoundly impacted human and animal populations. Reconstructing a map of the LGM will not be a easy process; it requires piecing collectively an enormous puzzle of fragmented information from numerous sources. Nevertheless, the ensuing maps supply invaluable insights into previous climates, ecosystems, and the forces that formed our world. This text explores the challenges and successes of mapping the LGM, highlighting the important thing options of those ice age maps and their implications for understanding our planet’s dynamic historical past.
The Challenges of Reconstructing a Glacial World:
Creating an correct map of the LGM presents a number of important challenges. Firstly, the ice sheets themselves left behind restricted direct proof. Whereas glacial deposits like moraines and until present clues to ice extent, these options are sometimes obscured by later geological processes. Secondly, the ice sheets weren’t static; they superior and retreated over millennia, abandoning a fancy file of deposition and erosion. Due to this fact, pinpointing the exact most extent of the ice requires cautious evaluation of a number of datasets.
Thirdly, information availability varies considerably throughout the globe. Detailed geological surveys exist for some areas, significantly in North America and Europe, whereas others, particularly in high-latitude and distant areas, stay poorly understood. This uneven distribution of information creates biases within the reconstructed maps. Lastly, decoding the oblique proof, equivalent to sea degree modifications, vegetation shifts, and modifications in animal populations, requires refined modeling methods and an understanding of complicated suggestions mechanisms throughout the Earth system.
Information Sources for LGM Mapping:
Regardless of these challenges, important progress has been made in mapping the LGM. This progress depends on a mixture of information sources:
-
Geological Proof: This contains direct observations of glacial landforms like moraines, drumlins, and eskers, which mark the bounds of previous ice sheets. Evaluation of glacial sediments, together with until and varves, supplies details about ice thickness and movement patterns. The presence of particular rock sorts transported by glaciers (erratics) also can point out the course and distance of ice motion.
-
Geophysical Information: Seismic surveys, ground-penetrating radar, and gravity measurements assist to map the subsurface extent of glacial deposits and the underlying bedrock topography. That is significantly essential in areas the place floor options are obscured by vegetation or later sedimentation.
-
Sea Degree Information: In the course of the LGM, huge quantities of water had been locked up in ice sheets, inflicting international sea ranges to drop by roughly 120 meters. The extent of submerged coastal options, equivalent to historical shorelines and submerged river valleys, supplies essential details about previous sea ranges and ice quantity. Evaluation of coral reefs and different marine sediments additionally contributes to this understanding.
-
Paleobotanical and Paleozoological Information: Pollen evaluation (palynology) reveals modifications in vegetation patterns, reflecting shifts in temperature and precipitation. Fossil stays of crops and animals present additional insights into previous ecosystems and weather conditions. The distribution of particular species can point out the presence of specific habitats and climatic zones.
-
Local weather Modeling: Subtle local weather fashions combine varied information sources to simulate previous climates and predict the extent of ice sheets. These fashions account for components equivalent to photo voltaic radiation, atmospheric composition, and ocean currents. Nevertheless, the accuracy of those fashions is determined by the standard and completeness of the enter information.
Key Options of LGM Maps:
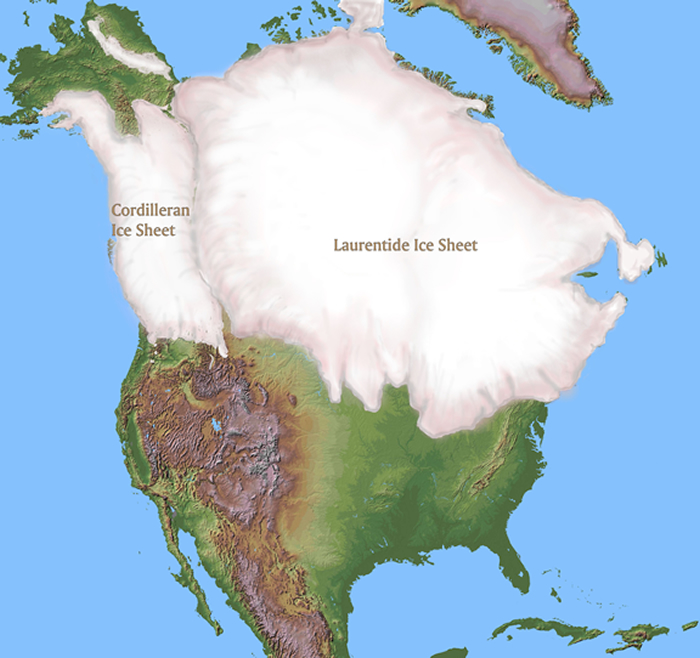
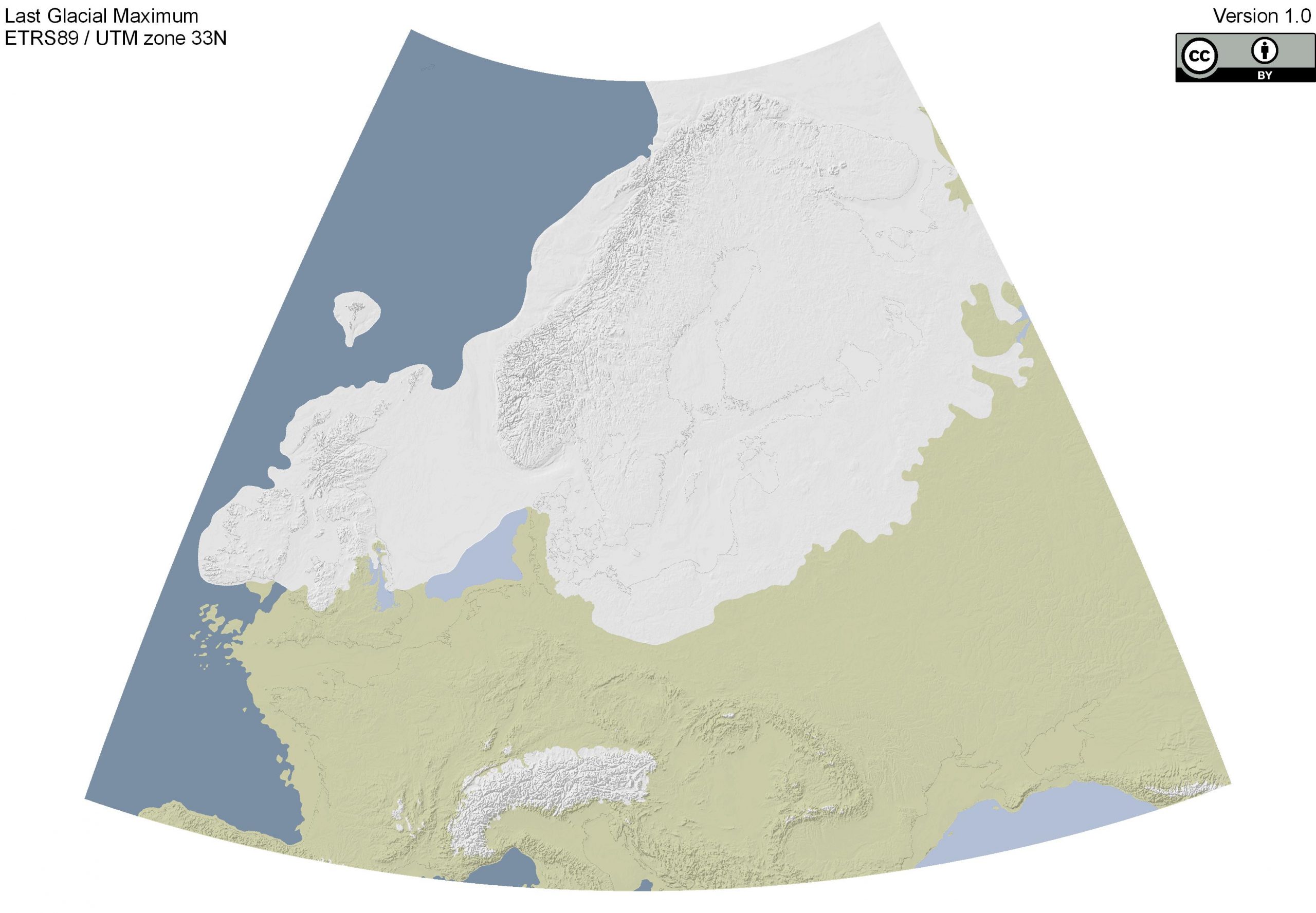
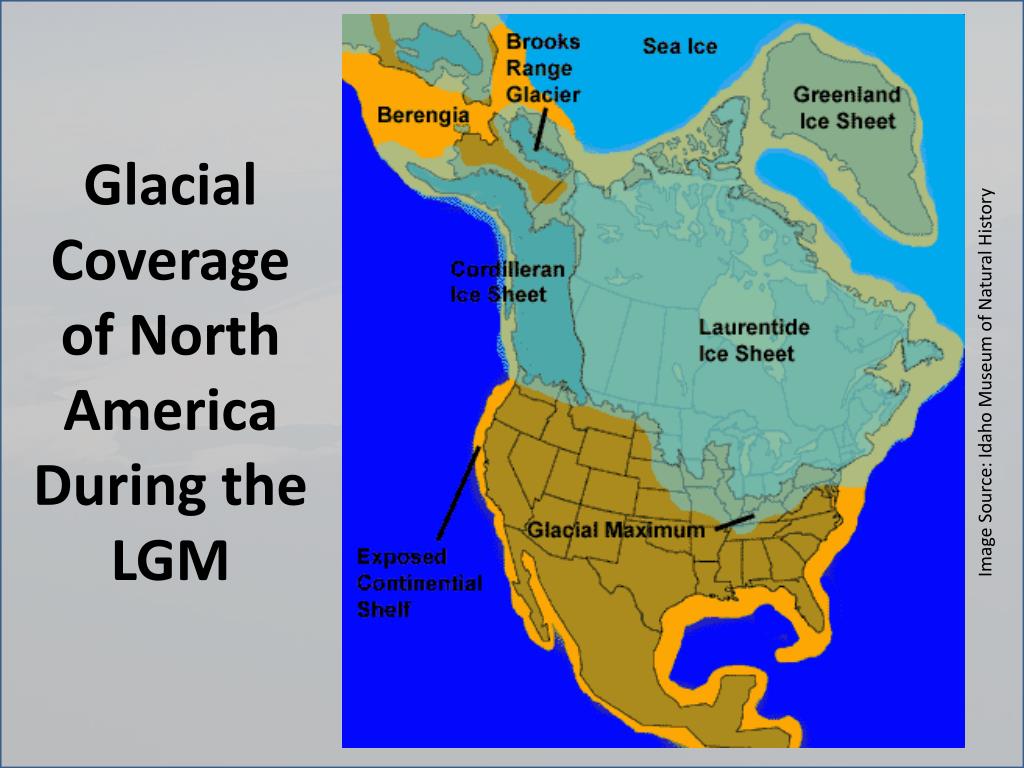
LGM maps reveal a dramatically totally different world in comparison with at present. Probably the most hanging characteristic is the huge extent of continental ice sheets. In North America, the Laurentide Ice Sheet coated a lot of Canada and prolonged south into the US, reaching so far as the Ohio and Missouri Rivers. In Europe, the Scandinavian Ice Sheet coated Scandinavia, the British Isles, and components of northern Germany and Poland. The Patagonian Ice Sheet in South America additionally expanded considerably.
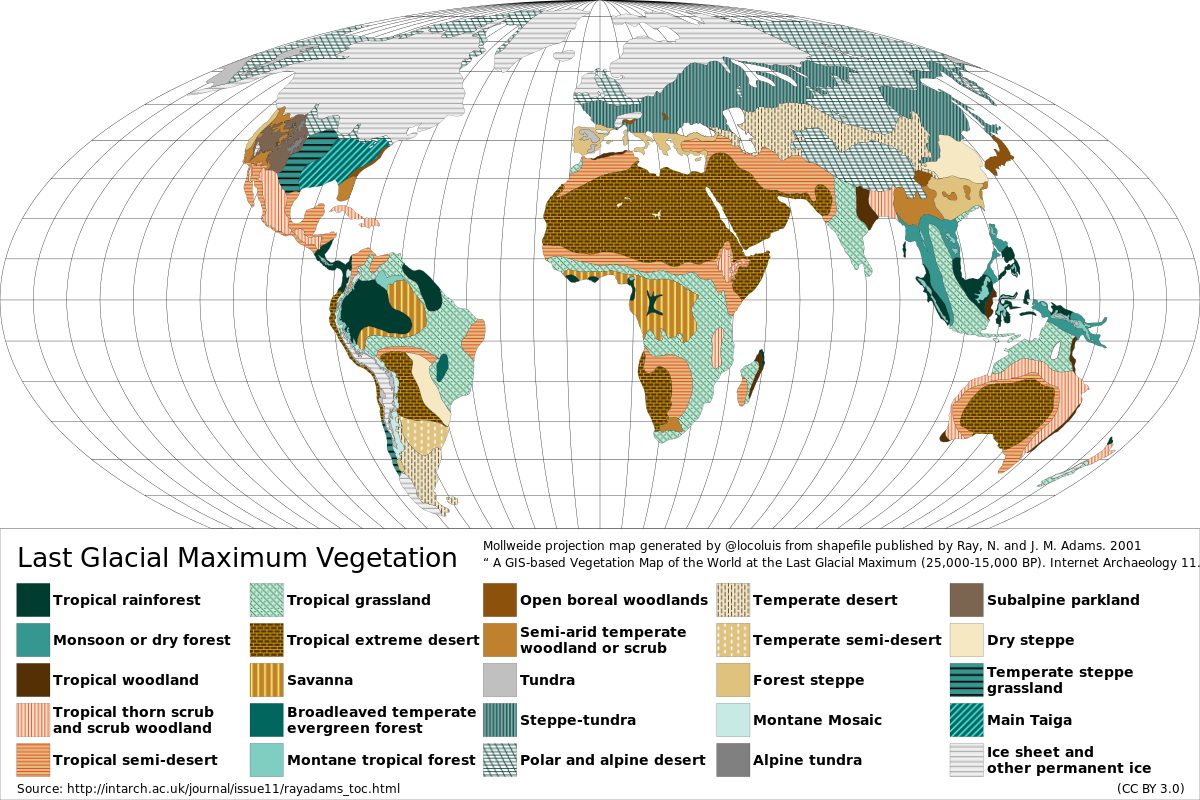
These ice sheets profoundly altered drainage patterns, creating huge proglacial lakes and redirecting rivers. Sea degree was considerably decrease, exposing giant areas of continental shelf. The Bering Land Bridge, connecting Asia and North America, was uncovered, permitting for the migration of people and animals. Moreover, the maps reveal important modifications in vegetation zones, with tundra and boreal forests extending a lot additional south than they do at present. Desert areas had been usually extra intensive, reflecting modifications in atmospheric circulation patterns.
Implications and Ongoing Analysis:
LGM maps will not be simply historic curiosities; they’ve important implications for understanding present-day local weather change. By finding out the previous responses of the Earth system to local weather forcing, scientists can refine local weather fashions and enhance predictions for future local weather situations. Understanding the dynamics of previous ice sheets is essential for assessing the potential for future sea degree rise. Moreover, the research of previous ecosystems supplies insights into the resilience and vulnerability of species to environmental change.
Analysis on the LGM continues, with ongoing efforts to enhance the accuracy and backbone of maps. Advances in distant sensing methods, improved relationship strategies, and extra refined local weather fashions are contributing to a extra refined understanding of this crucial interval in Earth’s historical past. The combination of various information sources, utilizing methods equivalent to Bayesian inference and machine studying, can be resulting in extra sturdy and complete maps.
Conclusion:
Mapping the Final Glacial Most is a fancy however essential endeavor. The ensuing maps present a window right into a dramatically totally different world, revealing the facility of ice sheets to reshape landscapes and profoundly impression ecosystems. Whereas challenges stay, ongoing analysis is steadily bettering our understanding of the LGM, offering precious insights into previous local weather dynamics and informing our understanding of current and future local weather change. The continued refinement of LGM maps will stay a significant device for scientists searching for to grasp the Earth’s intricate and dynamic historical past and to foretell its future. The journey into the frozen previous continues, revealing new insights with every advance in expertise and analysis methodology.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered precious insights into Mapping the Final Glacial Most: A Journey into the Frozen Previous. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!