The Brazos River, a lifeline weaving through the heart of Texas, is more than just a body of water. It’s a historical artery, an ecological treasure, and a vital resource for agriculture, industry, and recreation. To truly grasp its significance, understanding its geography is paramount, and this understanding is best achieved through the study of Brazos River maps. These maps, in their various forms, provide a comprehensive visual representation of the river’s journey, its tributaries, the surrounding landscape, and the human impact it has shaped.
From historical charts depicting early explorations to modern-day hydrological surveys, Brazos River maps offer a multi-faceted perspective on this iconic waterway. They reveal the river’s origin, its winding course, the diverse terrain it traverses, and the communities that thrive along its banks. This article will delve into the world of Brazos River maps, exploring their different types, their historical evolution, the valuable information they contain, and the importance of interpreting them effectively.
A Tapestry of Maps: Exploring the Different Types
The term "Brazos River map" encompasses a wide variety of cartographic representations, each serving a specific purpose and highlighting different aspects of the river and its surroundings. Some of the most common types include:
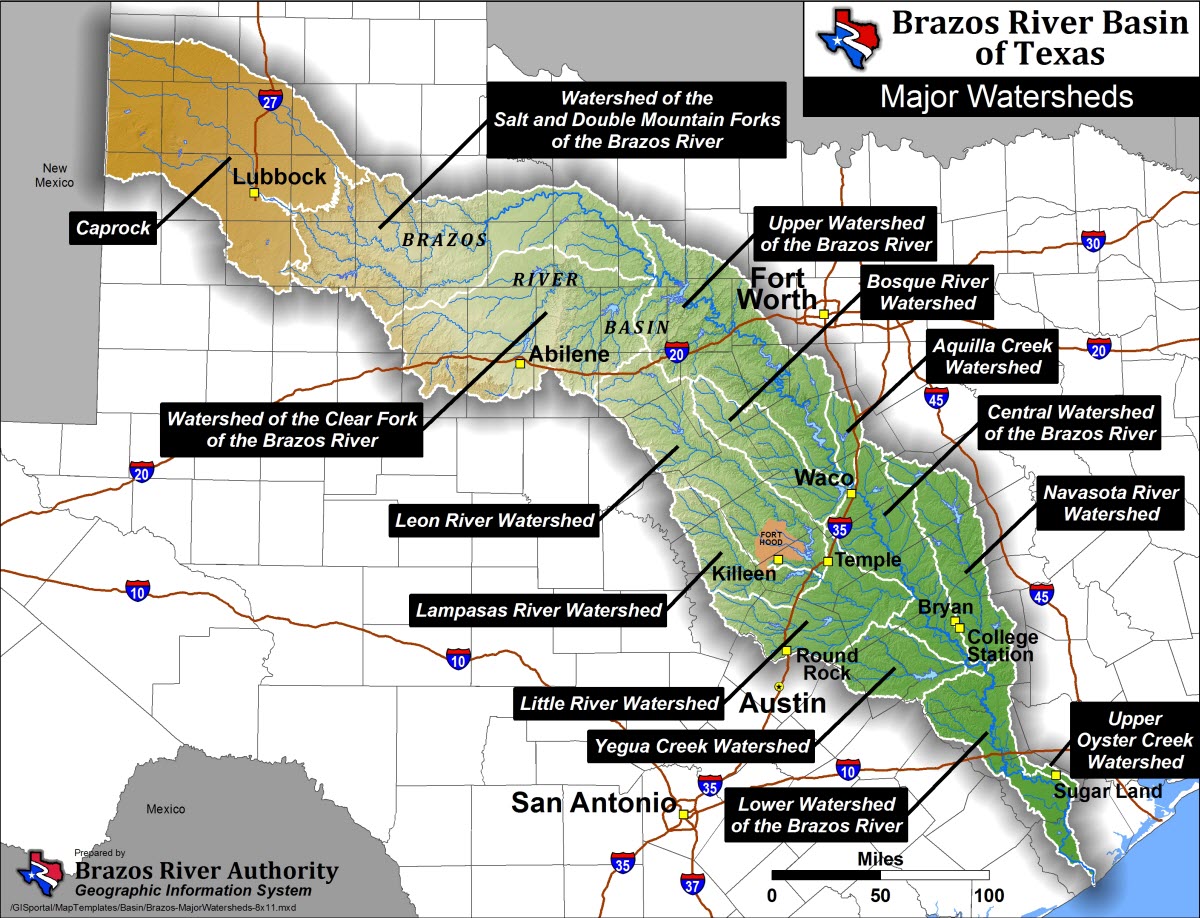
- Topographic Maps: These maps depict the physical features of the land, including elevation, relief, and landforms. They show the river’s course in relation to mountains, valleys, and plains, providing a crucial understanding of its drainage basin and the surrounding topography. US Geological Survey (USGS) topographic maps are particularly valuable for detailed analysis.
- Hydrological Maps: Focusing specifically on water resources, hydrological maps illustrate the river’s drainage network, including its tributaries, reservoirs, and aquifers. They often display information about water quality, flow rates, and groundwater levels, crucial for water management and conservation efforts.
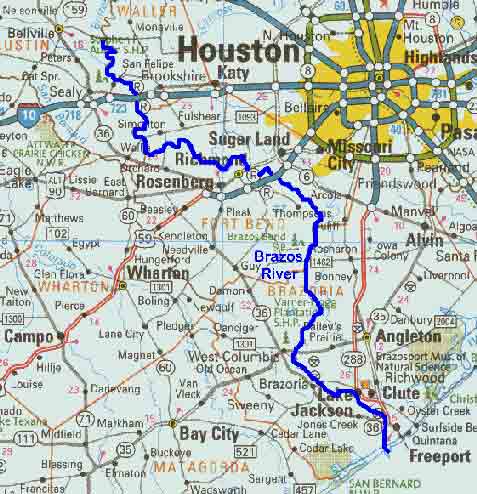
- Navigation Charts: Designed for boaters and navigators, these charts provide detailed information about the river’s depth, channel markings, hazards, and navigational aids. They are essential for safe and efficient river travel, particularly in areas with shallow waters or obstructions.
- Historical Maps: These maps offer a glimpse into the past, showcasing the river’s course and surrounding settlements as they existed in different eras. They can reveal how the river has changed over time due to natural processes or human interventions, and how early explorers and settlers interacted with the waterway. Examples include maps from Spanish explorers and early Texas land surveys.
- Land Use Maps: These maps illustrate how the land surrounding the river is being used, including agriculture, urban development, industrial areas, and protected areas. They help to understand the impact of human activities on the river’s ecosystem and water quality.
- Geological Maps: These maps depict the underlying geological formations of the region, revealing the types of rocks and soils that influence the river’s course and water chemistry. They are valuable for understanding the river’s erosion patterns and the potential for groundwater contamination.
- Interactive Online Maps: With the advent of technology, interactive online maps have become increasingly popular. These maps allow users to zoom in and out, overlay different layers of information, and access real-time data about the river’s conditions. They often incorporate satellite imagery, aerial photography, and Geographic Information System (GIS) data.
A Journey Through Time: The Historical Evolution of Brazos River Maps
The history of Brazos River maps mirrors the history of Texas itself. Early maps were often rudimentary and based on limited exploration, reflecting the challenges faced by early explorers and settlers in navigating the vast and unfamiliar territory.
- Early Explorations: Spanish explorers like Álvar Núñez Cabeza de Vaca were among the first Europeans to encounter the Brazos River in the 16th century. While their maps were not precise, they marked the river’s presence and contributed to the growing understanding of the region.
- French Influence: René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle, explored the Texas coast in the late 17th century, and his maps, though inaccurate in some respects, further documented the major rivers, including the Brazos.
- Early Texas Maps: As Texas began to attract settlers, land surveyors and cartographers created more detailed maps to delineate property boundaries and document the region’s resources. These maps often highlighted the importance of the Brazos River as a transportation route and a source of water.
- 19th Century Developments: The 19th century saw significant advancements in cartography, with the introduction of improved surveying techniques and printing methods. Maps of the Brazos River became more accurate and detailed, reflecting the growing population and economic development of the region.
- Modern Mapping Technologies: The 20th and 21st centuries have witnessed a revolution in mapping technologies, with the advent of aerial photography, satellite imagery, and GIS. These technologies have enabled the creation of highly accurate and detailed maps of the Brazos River, providing valuable insights for water management, environmental conservation, and urban planning.
Unlocking the Information: Interpreting Brazos River Maps
To effectively utilize Brazos River maps, it’s crucial to understand the basic principles of map interpretation. This includes understanding map symbols, scales, legends, and coordinate systems.
- Map Symbols: Maps use a variety of symbols to represent different features, such as rivers, roads, buildings, and vegetation. Understanding these symbols is essential for accurately interpreting the map’s information.
- Map Scale: The map scale indicates the relationship between the distance on the map and the corresponding distance on the ground. A large-scale map shows a smaller area in greater detail, while a small-scale map shows a larger area with less detail.
- Map Legend: The map legend, or key, explains the meaning of the symbols and colors used on the map. It is an essential tool for understanding the map’s information.
- Coordinate Systems: Maps use coordinate systems, such as latitude and longitude, to define the location of features on the Earth’s surface. Understanding these systems allows for precise location identification and measurement.
Beyond these basic elements, understanding the context in which a map was created is vital. Who created the map? What was their purpose? What data sources did they use? These questions can help to assess the map’s accuracy and reliability.
The Brazos River: A Resource Worth Mapping
Brazos River maps are not just historical artifacts or academic tools; they are essential resources for a wide range of applications.
- Water Management: Hydrological maps and data are critical for managing the river’s water resources, including allocating water rights, monitoring water quality, and planning for drought and flood events.
- Environmental Conservation: Maps can help to identify sensitive ecosystems along the river, monitor the impact of human activities, and develop conservation strategies to protect the river’s biodiversity.
- Urban Planning: Land use maps and topographic maps are essential for planning urban development along the river, ensuring that development is sustainable and minimizes its impact on the river’s ecosystem.
- Recreation and Tourism: Navigation charts and recreational maps provide valuable information for boaters, anglers, and other outdoor enthusiasts, promoting safe and enjoyable river experiences.
- Historical Research: Historical maps offer valuable insights into the past, helping to understand the river’s role in shaping the history and culture of Texas.
Conclusion: The Enduring Value of Brazos River Maps
Brazos River maps, in their diverse forms and historical contexts, offer a powerful lens through which to understand this vital Texas waterway. From the early explorations that charted its course to the modern technologies that monitor its flow, these maps provide invaluable insights into the river’s geography, ecology, and human significance. By understanding the different types of maps, their historical evolution, and the principles of map interpretation, we can unlock the wealth of information they contain and use it to protect, manage, and appreciate this iconic Texas resource for generations to come. The Brazos River is more than just a river; it’s a story etched onto the landscape, and maps are the keys to deciphering that story.
/cloudfront-us-east-1.images.arcpublishing.com/gray/R45LQFXCKJF4JMLSGLJY6WZ3RI.jpg)



