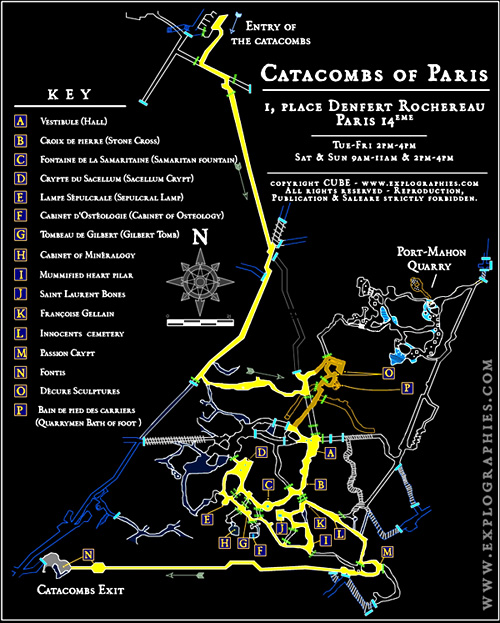
Catacombs, those subterranean ossuaries, have held a morbid fascination for centuries. More than just mass graves, they are intricate networks, often sprawling labyrinths carved into the earth, imbued with history, mystery, and the echoes of past civilizations. Understanding these subterranean worlds requires more than just a flashlight and a sense of adventure; it requires a map. The catacombs map, a vital tool for explorers, researchers, and anyone interested in the history and cultural significance of these underground realms, provides a crucial guide to navigating their complex layouts and deciphering their secrets.
This article delves into the fascinating world of catacombs maps, exploring their history, purpose, evolution, and the challenges involved in their creation and interpretation. We will examine the different types of maps, the information they contain, and the importance they play in preserving and understanding these unique historical sites.
A History Etched in Stone: The Origins of Catacombs Maps
The history of catacombs maps is intertwined with the history of the catacombs themselves. Early Christians, facing persecution in the Roman Empire, often sought refuge in underground cemeteries and tombs, expanding existing networks or creating new ones. These early catacombs were primarily functional, serving as burial sites and places of worship. However, as their complexity grew, the need for some form of orientation became apparent.
While formal, meticulously drawn maps were likely absent in the earliest days, it’s plausible that simple sketches or markings were used to navigate the narrow passageways. These crude maps, perhaps etched onto walls or maintained in memory, would have served as essential tools for remembering the locations of specific tombs, escape routes, and meeting places.
The rise of Christianity and the cessation of persecution led to a period of relative neglect for the catacombs. Over time, knowledge of their layouts faded, and the entranceways were often obscured or lost. However, a renewed interest in the catacombs emerged during the Renaissance, driven by a desire to understand early Christian history and recover relics.
This resurgence of interest spurred the creation of the first formal catacombs maps. These early maps, often produced by archaeologists, scholars, and even treasure hunters, were far from perfect. They were often based on limited exploration, relying on guesswork and inaccurate measurements. Nevertheless, they represented a crucial first step in documenting and understanding these complex underground systems.
The Purpose of the Map: Navigation, Research, and Preservation
The primary purpose of a catacombs map is, undoubtedly, navigation. These networks can be incredibly disorienting, with winding passages, dead ends, and multiple levels. A map provides a crucial framework for understanding the overall layout, identifying key landmarks, and avoiding getting lost.
However, the utility of a catacombs map extends far beyond simple navigation. They serve as invaluable tools for:
- Archaeological Research: Maps are essential for documenting the structure and organization of the catacombs, allowing researchers to understand how they were built, expanded, and used over time. They help in identifying different burial chambers, analyzing the distribution of tombs, and understanding the social organization of the communities that used them.
- Historical Interpretation: By mapping the locations of specific inscriptions, artworks, and artifacts, researchers can gain insights into the beliefs, practices, and artistic styles of the people who built and used the catacombs.
- Preservation and Conservation: Accurate maps are crucial for monitoring the condition of the catacombs and identifying areas that are at risk of collapse or damage. They allow conservators to plan and implement effective preservation strategies.
- Tourism and Education: Detailed maps can be used to create informative tours for visitors, allowing them to explore the catacombs in a safe and engaging manner. They also serve as valuable educational resources, providing insights into the history, art, and architecture of these fascinating sites.
- Security: Maps can be used to monitor access points and identify potential security threats, helping to protect the catacombs from vandalism and unauthorized entry.
Types of Catacombs Maps: From Hand-Drawn Sketches to Digital Models
Catacombs maps have evolved significantly over time, reflecting advancements in technology and surveying techniques. Different types of maps offer varying levels of detail and accuracy, each suited to specific purposes:
- Hand-Drawn Maps: These are the earliest forms of catacombs maps, often created by explorers, archaeologists, and scholars. They are typically based on visual observation and simple measurements, and can vary widely in accuracy and detail. While often less precise, they can offer valuable insights into the perspectives and priorities of the people who created them.
- Survey Maps: These maps are created using surveying instruments, such as compasses, theodolites, and levels, to obtain accurate measurements of the catacombs. They provide a more precise representation of the layout, including the locations of walls, passages, and other features.
- Photogrammetric Maps: Photogrammetry involves using photographs to create three-dimensional models of objects or spaces. This technique can be used to create highly detailed and accurate maps of catacombs, capturing the intricate details of the walls, ceilings, and floors.
- Laser Scanning Maps: Laser scanning, also known as LiDAR (Light Detection and Ranging), uses lasers to measure the distance to objects. This technique can be used to create incredibly detailed three-dimensional models of catacombs, capturing even the smallest features with millimeter accuracy.
- Digital Maps and GIS (Geographic Information System): Modern mapping relies heavily on digital technologies. GIS allows for the integration of various data sources, including survey data, photographs, laser scans, and historical records, to create interactive maps that can be used for research, preservation, and tourism. Digital maps can be easily updated and shared, making them invaluable tools for managing and understanding catacombs.
Challenges in Mapping the Underground: Obstacles to Accurate Representation
Mapping catacombs is a challenging endeavor, fraught with obstacles that can hinder the creation of accurate and comprehensive maps. Some of the key challenges include:
- Limited Access: Catacombs are often difficult to access, with narrow passageways, low ceilings, and unstable ground. This can make it challenging to move around and take measurements.
- Darkness and Humidity: The darkness and humidity of the catacombs can affect the accuracy of surveying instruments and make it difficult to see and record details.
- Complex Layouts: The intricate and often irregular layouts of catacombs can make it difficult to create accurate maps. Winding passages, dead ends, and multiple levels can create confusion and make it challenging to maintain orientation.
- Instability: Many catacombs are in a state of disrepair, with collapsing walls, unstable ceilings, and loose debris. This can make it dangerous to explore and map them.
- Limited Resources: Mapping catacombs can be expensive, requiring specialized equipment, skilled personnel, and significant time. Funding for mapping projects is often limited, which can hinder progress.
- Incomplete Information: In many cases, historical records and existing maps are incomplete or inaccurate. This can make it difficult to reconstruct the original layout of the catacombs and understand their history.
Interpreting the Map: Unveiling the Stories Buried Below
A catacombs map is more than just a representation of space; it’s a key to unlocking the stories buried within the earth. By studying the map, researchers can gain insights into the history, culture, and beliefs of the people who built and used the catacombs.
The location of tombs, the inscriptions they bear, and the artwork that adorns them can reveal information about the social status, religious beliefs, and artistic tastes of the individuals buried within. The layout of the catacombs themselves can provide clues about the organization of the community and the way they used the space for burial, worship, and other activities.
Furthermore, comparing maps of different catacombs can reveal similarities and differences in their construction and use, providing insights into the evolution of burial practices and the spread of religious ideas.
The Future of Catacombs Mapping: Technology and Preservation
The future of catacombs mapping is bright, with advancements in technology promising to revolutionize the way we explore and understand these underground worlds. Laser scanning, photogrammetry, and GIS are becoming increasingly sophisticated, allowing for the creation of incredibly detailed and accurate maps.
These technologies are also being used to develop virtual reality (VR) and augmented reality (AR) experiences that allow users to explore catacombs from the comfort of their own homes. These immersive experiences can provide a unique and engaging way to learn about the history and culture of these fascinating sites.
Furthermore, advancements in robotics are making it possible to explore and map catacombs that are too dangerous or inaccessible for humans. Robots equipped with cameras, sensors, and mapping equipment can navigate narrow passages, climb over obstacles, and collect data that can be used to create detailed maps.
Ultimately, the ongoing efforts to map and document catacombs are essential for preserving these unique historical sites for future generations. By understanding their structure, history, and significance, we can ensure that they are protected from damage, vandalism, and neglect, allowing them to continue to inspire and inform us for centuries to come. The catacombs map, therefore, is not just a guide to the underworld, but a testament to the enduring power of human curiosity and the importance of preserving our shared cultural heritage.