A Shattered Continent: Mapping Europe in 1919 and the Legacy of the Nice Conflict
Associated Articles: A Shattered Continent: Mapping Europe in 1919 and the Legacy of the Nice Conflict
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to A Shattered Continent: Mapping Europe in 1919 and the Legacy of the Nice Conflict. Let’s weave fascinating info and supply contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
A Shattered Continent: Mapping Europe in 1919 and the Legacy of the Nice Conflict

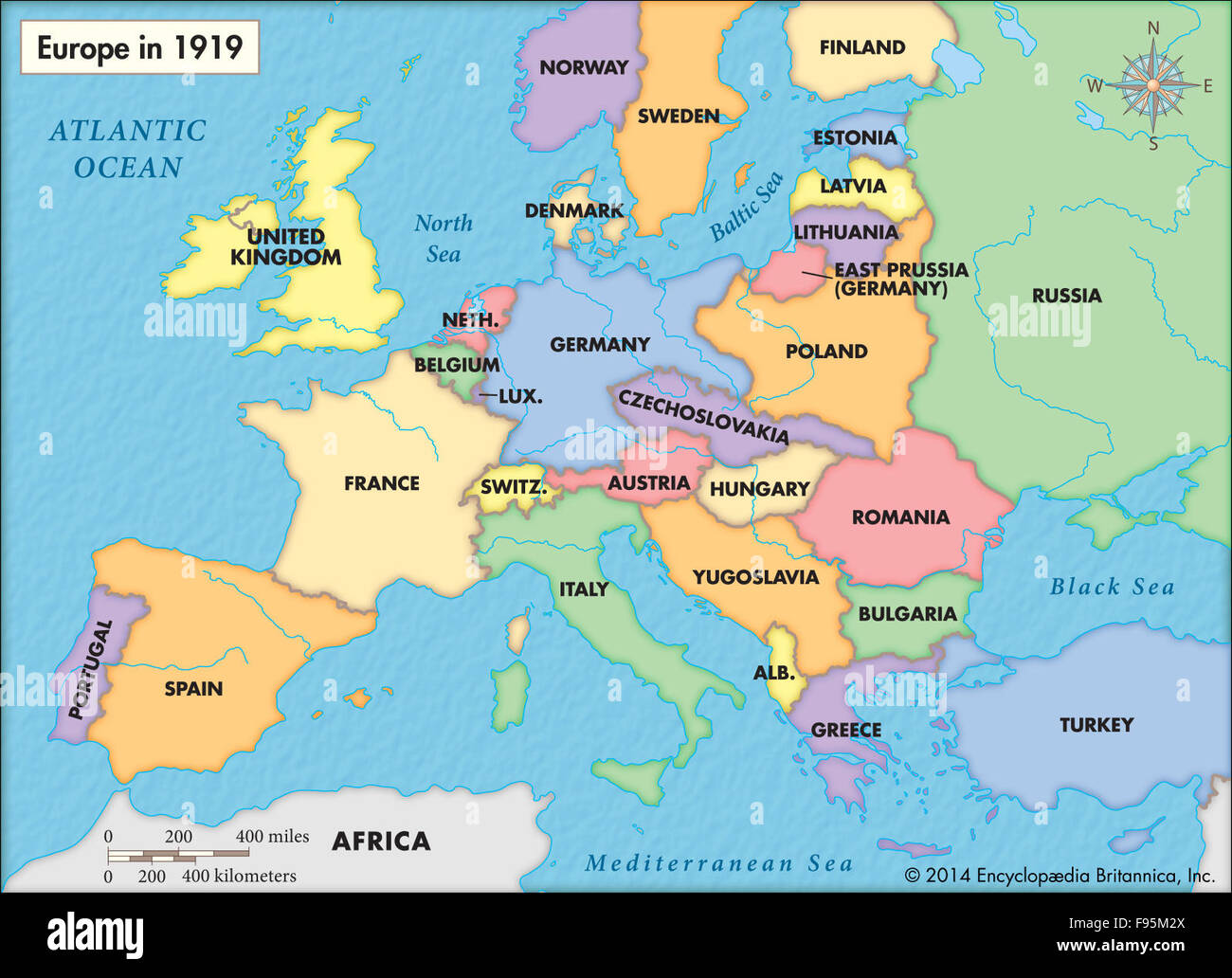
The 12 months 1919 witnessed a Europe irrevocably reworked. The Nice Conflict, a battle of unprecedented scale and brutality, had concluded, leaving in its wake a continent scarred bodily and psychologically. The map of Europe, as soon as a comparatively secure patchwork of empires and nations, was redrawn within the aftermath of the Treaty of Versailles and different associated agreements, reflecting the dramatic shifts in energy and the aspirations of newly unbiased states. Analyzing the 1919 map of Europe reveals not solely the rapid penalties of the battle but additionally the seeds of future conflicts and the enduring legacy of this tumultuous interval.
Probably the most putting function of the 1919 map is the dismantling of the three nice empires: the German, Austro-Hungarian, and Russian. The German Empire, as soon as a formidable navy and industrial energy, was considerably gotten smaller and affect. Alsace-Lorraine, misplaced to France in 1871, was returned, and vital territories within the east, together with elements of Prussia and Silesia, have been ceded to Poland and the newly created Czechoslovakia. The German colonies in Africa and the Pacific have been mandated to different Allied powers, successfully ending German colonial ambitions. This territorial loss, coupled with crippling reparations imposed by the Treaty of Versailles, fueled resentment and contributed to the rise of extremism in Germany in the course of the interwar interval. The map displays a deliberate try by the Allied powers to weaken Germany, stopping future aggression, however this strategy in the end proved counterproductive.
The Austro-Hungarian Empire, a multi-ethnic conglomerate, fragmented into a number of unbiased states. Austria and Hungary, tremendously diminished in measurement and inhabitants, emerged as separate nations. Czechoslovakia, a brand new nation incorporating Bohemia, Moravia, and Slovakia, was established, reflecting the aspirations of the Slavic populations throughout the former empire. Yugoslavia, a union of South Slavic peoples, additionally got here into existence, though its inner divisions and conflicting nationwide identities foreshadowed future instability. The disintegration of the Austro-Hungarian Empire considerably altered the ethnic map of Central Europe, creating new nationwide borders that usually did not align with ethnic realities, resulting in vital minority populations inside newly shaped states. This advanced ethnic mosaic would change into a supply of rigidity and battle within the many years to come back.
The Russian Empire, already weakened by inner revolutions and civil battle, underwent probably the most radical transformation. The Bolshevik victory within the Russian Civil Conflict led to the institution of the Soviet Union, an unlimited communist state encompassing a good portion of the previous Russian Empire. Nonetheless, the map in 1919 did not absolutely replicate the extent of Soviet management, because the borders remained fluid and contested all through the early years of the Soviet regime. Finland, Poland, the Baltic states (Estonia, Latvia, Lithuania), and elements of Ukraine and Belarus gained independence, making a buffer zone between Soviet Russia and the remainder of Europe. This newly unbiased territory was usually unstable, experiencing inner conflicts and exterior pressures from each Soviet Russia and its neighbors. The emergence of the Soviet Union, with its revolutionary ideology and expansionist ambitions, basically altered the geopolitical panorama of Europe, setting the stage for the Chilly Conflict.
The 1919 map additionally displays the redrawing of borders within the Balkans, a area already characterised by ethnic complexity and historic rivalries. The Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine imposed vital territorial losses on Bulgaria, whereas Greece gained territory in Thrace and elements of Macedonia. The borders drawn within the Balkans, nonetheless, remained contested and unstable, contributing to continued tensions and conflicts within the area. The creation of Yugoslavia, whereas meant to unify South Slavic peoples, proved a difficult endeavor, as competing nationalisms and historic grievances throughout the new state hindered its stability.
Past the most important territorial modifications, the 1919 map reveals the institution of the League of Nations, a world group aimed toward stopping future wars by means of diplomacy and collective safety. Whereas the League’s success was in the end restricted, its creation mirrored a post-war need for worldwide cooperation and a recognition of the necessity for a brand new world order. The map, due to this fact, not solely depicts the bodily modifications in Europe but additionally symbolizes the aspirations and failures of the post-war settlement.
The map of 1919 was not a static entity. The borders drawn within the aftermath of the battle have been usually arbitrary and did not adequately replicate the advanced ethnic realities of the area. Minority populations discovered themselves immediately a part of new states, usually dealing with discrimination and political marginalization. The Treaty of Versailles, whereas meant to create an enduring peace, sowed the seeds of future battle, significantly in Germany, the place resentment over territorial losses and reparations fueled nationalist and revisionist actions.
Moreover, the rise of fascism and Nazism within the interwar interval additional destabilized the post-war order. These ideologies exploited the financial hardships and political instability of the time, difficult the present boundaries and in the end resulting in the outbreak of World Conflict II. The map of 1919, due to this fact, serves as a reminder of the fragility of peace and the enduring affect of unresolved conflicts.
In conclusion, the 1919 map of Europe is a strong visible illustration of the profound penalties of the Nice Conflict. It illustrates the dismantling of empires, the emergence of recent nations, and the redrawing of borders primarily based on usually conflicting nationwide aspirations and geopolitical issues. Whereas the map mirrored a need for a secure and peaceable Europe, it additionally contained the seeds of future conflicts, revealing the constraints of the post-war settlement and the enduring challenges of nation-building and worldwide cooperation in a continent scarred by battle. The examine of this map gives invaluable insights into the complexities of European historical past and the lasting legacy of the First World Conflict, reminding us of the fragility of peace and the significance of understanding the historic context of up to date geopolitical points. The 1919 map, due to this fact, stays an important historic doc, providing a window right into a pivotal second in European historical past and its lasting repercussions.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into A Shattered Continent: Mapping Europe in 1919 and the Legacy of the Nice Conflict. We hope you discover this text informative and useful. See you in our subsequent article!