Decoding the Hexagon: A Deep Dive into the Departmental Map of France
Associated Articles: Decoding the Hexagon: A Deep Dive into the Departmental Map of France
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing matter associated to Decoding the Hexagon: A Deep Dive into the Departmental Map of France. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Decoding the Hexagon: A Deep Dive into the Departmental Map of France
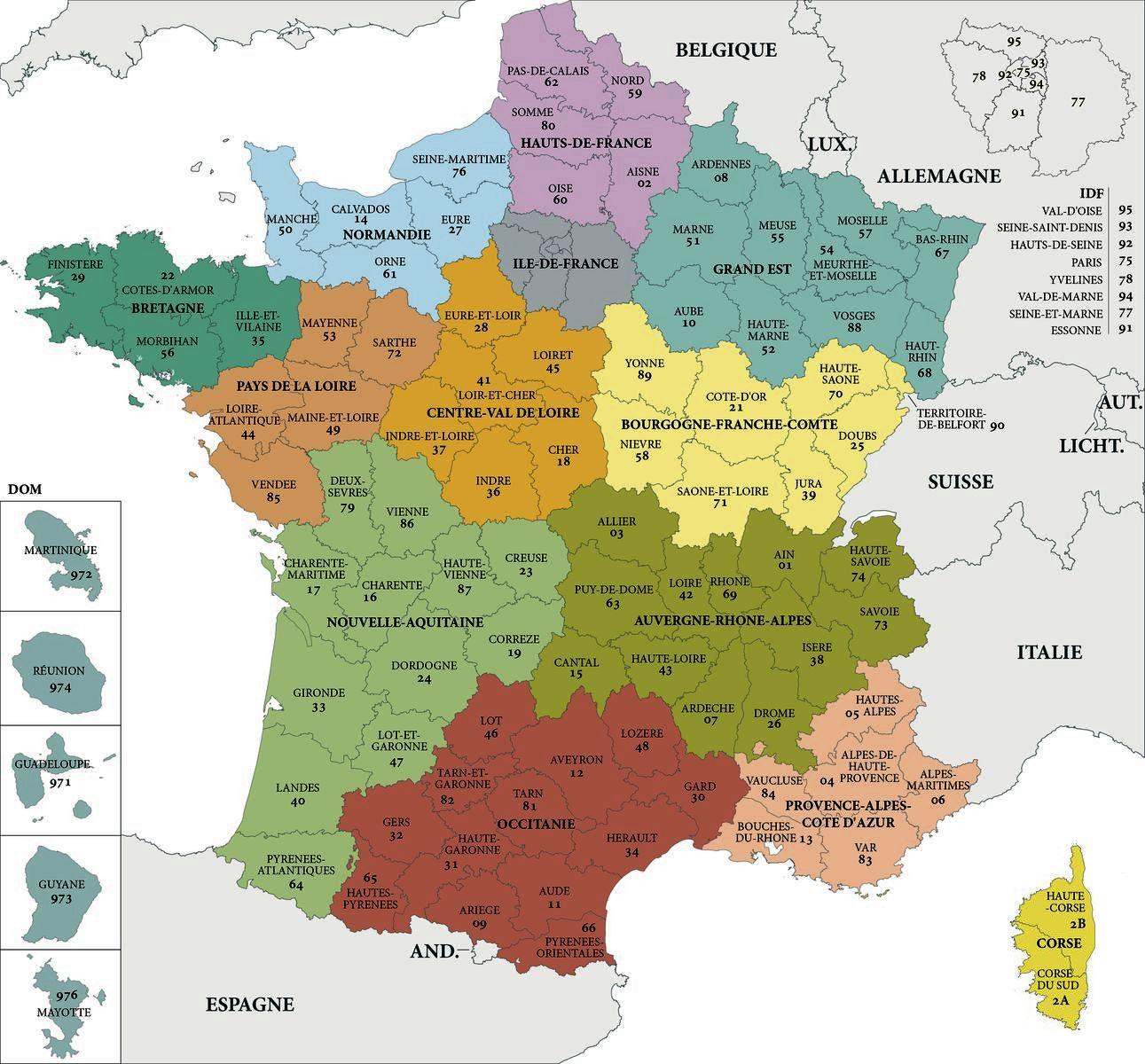
France, the "Hexagon" because it’s affectionately identified for its roughly hexagonal form, is a rustic of numerous landscapes, wealthy historical past, and a fancy administrative construction. Understanding this construction requires navigating its intricate departmental map, a patchwork of 101 departments (départements in French) that kind the spine of its regional group. This text will delve into the historical past, geography, and significance of those departments, exploring their position in French administration and offering insights into the fascinating tapestry they weave throughout the nation’s panorama.
A Historic Perspective: From Provinces to Departments
Earlier than the French Revolution, France was divided into provinces, historic entities with deep-rooted identities and infrequently conflicting loyalties to the crown. These provinces, remnants of centuries of conquest, inheritance, and political maneuvering, had been seen as obstacles to centralized energy and environment friendly governance. The revolution aimed to dismantle this feudal system and create a extra unified and equitable nation. The creation of departments in 1789-1790 was a vital step on this course of.
The Nationwide Constituent Meeting, pushed by Enlightenment beliefs of rationality and uniformity, designed the departmental system to switch the chaotic provincial construction. The purpose was to create comparatively equal-sized administrative models, facilitating the implementation of legal guidelines, taxation, and army mobilization throughout the nation. The departments had been numbered, largely from west to east, and named after geographical options, rivers, or historic occasions, eliminating the emotional baggage related to the outdated provinces. This rational strategy aimed to create a extra unified nationwide identification, transcending regional variations.
Nonetheless, the revolutionary fervor did not completely erase regional identities. Whereas the departments grew to become the first administrative models, the cultural and historic nuances of the previous provinces continued, subtly influencing native customs, dialects, and even political leanings. The departmental map, whereas designed for uniformity, displays the underlying geographical and historic realities of the French panorama.
Geographical Variations: A Patchwork of Landscapes
The 101 departments of France, every with its distinctive prefecture (administrative capital), show a outstanding range of geography. From the mountainous Pyrenees within the south to the rolling hills of Burgundy within the east, from the fertile plains of the Île-de-France to the rugged shoreline of Brittany, the departmental map displays the various topography of the nation. This geographical range is mirrored within the financial actions of every division, with some specializing in agriculture, others in trade, and nonetheless others in tourism.
The coastal departments, similar to these in Normandy, Brittany, and the Mediterranean, are characterised by their maritime actions, fishing, and tourism. The mountainous departments, like these within the Alps and Pyrenees, are identified for his or her snowboarding resorts and out of doors actions. The inland departments, typically situated in fertile valleys or plains, are predominantly agricultural, producing wine, cheese, and different agricultural merchandise. This intricate interaction between geography and financial exercise shapes the character of every division, contributing to the wealthy tapestry of French life.
Administrative Significance: The Division’s Position in Governance
Departments are essential elements of French native governance. They act as intermediaries between the central authorities and municipalities (communes), taking part in an important position within the implementation of nationwide insurance policies at an area degree. Every division has a prefect, appointed by the central authorities, who represents the state’s authority inside the division. The prefect oversees varied elements of departmental administration, together with public security, infrastructure, and the implementation of nationwide legal guidelines.
The departmental council (conseil départemental), an elected physique, is chargeable for managing departmental affairs, similar to social companies, schooling, and infrastructure tasks. The departmental council performs a big position in shaping the social and financial panorama of the division, allocating sources and implementing insurance policies aimed toward bettering the standard of life for its residents. This twin system, with the prefect representing the central authorities and the departmental council representing native pursuits, creates a stability between nationwide unity and regional autonomy.
Past Administration: Cultural and Regional Id
Whereas the departments had been created to advertise nationwide unity, they have not completely erased regional identities. Many departments retain sturdy connections to their historic provinces, mirrored of their cultural traditions, dialects, and even culinary specialties. The departmental map, subsequently, is not merely an administrative grid; it is also a mirrored image of France’s wealthy cultural range.
The departmental construction, whereas selling administrative effectivity, additionally facilitates the preservation and promotion of regional cultures. Many departments actively help native traditions, festivals, and cultural occasions, contributing to the colourful cultural panorama of France. The departmental map, on this sense, acts as a framework for each nationwide unity and regional expression, a fragile stability that has formed the identification of France for over two centuries.
The Abroad Departments: Extending the Hexagon
The departmental system extends past mainland France to incorporate 5 abroad departments (DOM): Guadeloupe, Martinique, French Guiana, Réunion, and Mayotte. These departments, whereas geographically distant, are integral components of the French Republic, having fun with the identical rights and duties as departments on the mainland. They signify a big side of France’s world presence and contribute to its cultural and financial range. Their inclusion within the departmental system underscores the enduring precept of nationwide unity, even throughout huge geographical distances.
Conclusion: A Dynamic Map in Fixed Evolution
The departmental map of France is greater than only a geographical illustration; it is a residing testomony to the nation’s historical past, its administrative construction, and its cultural range. From its revolutionary origins to its up to date position in governance, the departmental system has formed the French panorama and continues to evolve. Understanding this map is essential to comprehending the intricate workings of French society, its regional nuances, and its enduring quest for a stability between nationwide unity and regional identification. The seemingly easy strains on the map inform a fancy and interesting story of a nation consistently negotiating its previous and current, its middle and its peripheries, its uniformity and its range. The hexagon, subsequently, is way over a easy form; it’s a dynamic and ever-evolving reflection of the French nation itself.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied useful insights into Decoding the Hexagon: A Deep Dive into the Departmental Map of France. We hope you discover this text informative and helpful. See you in our subsequent article!
