Iceland: A Geographic Exploration By Maps
Associated Articles: Iceland: A Geographic Exploration By Maps
Introduction
On this auspicious event, we’re delighted to delve into the intriguing subject associated to Iceland: A Geographic Exploration By Maps. Let’s weave attention-grabbing info and provide recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Iceland: A Geographic Exploration By Maps
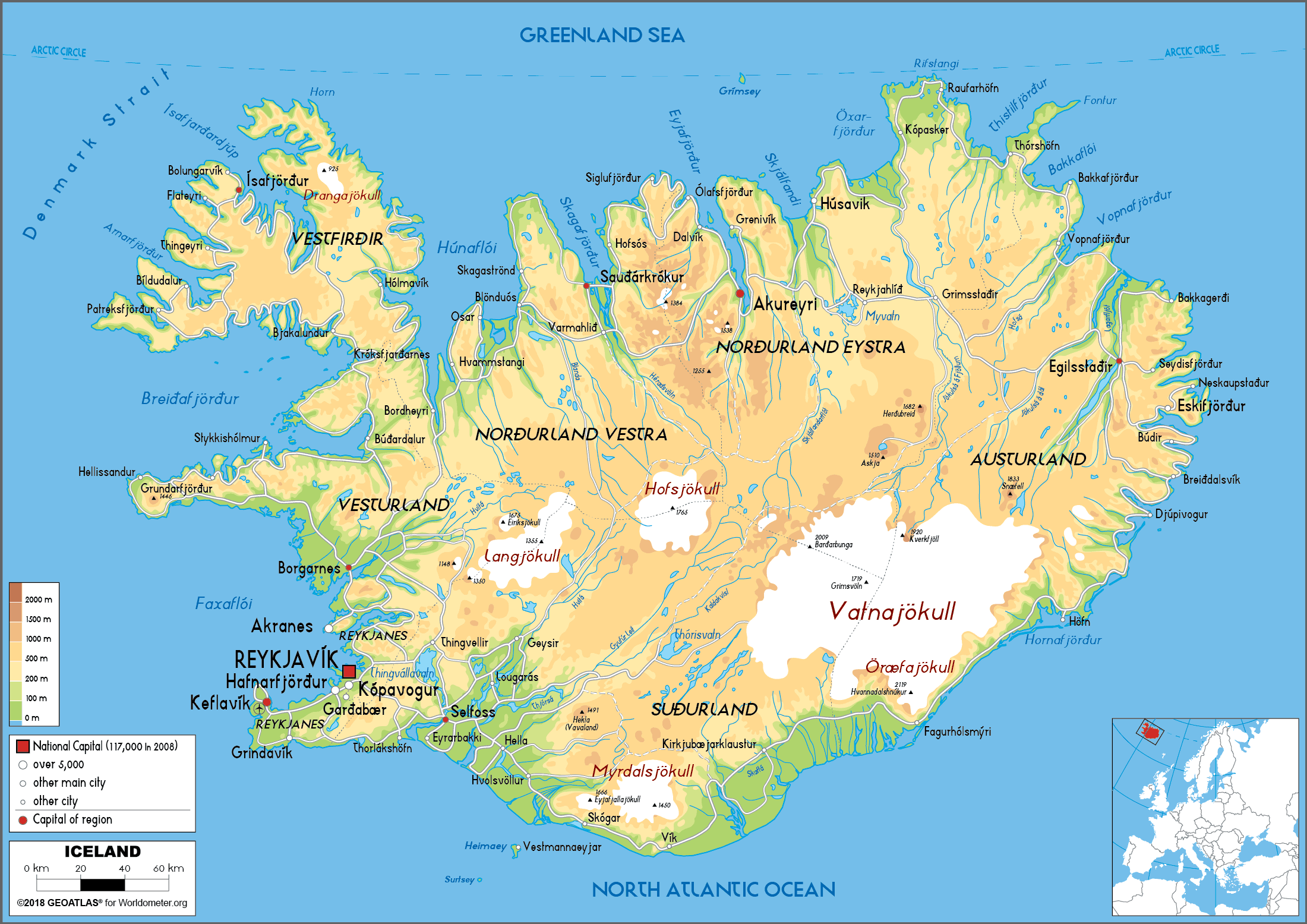
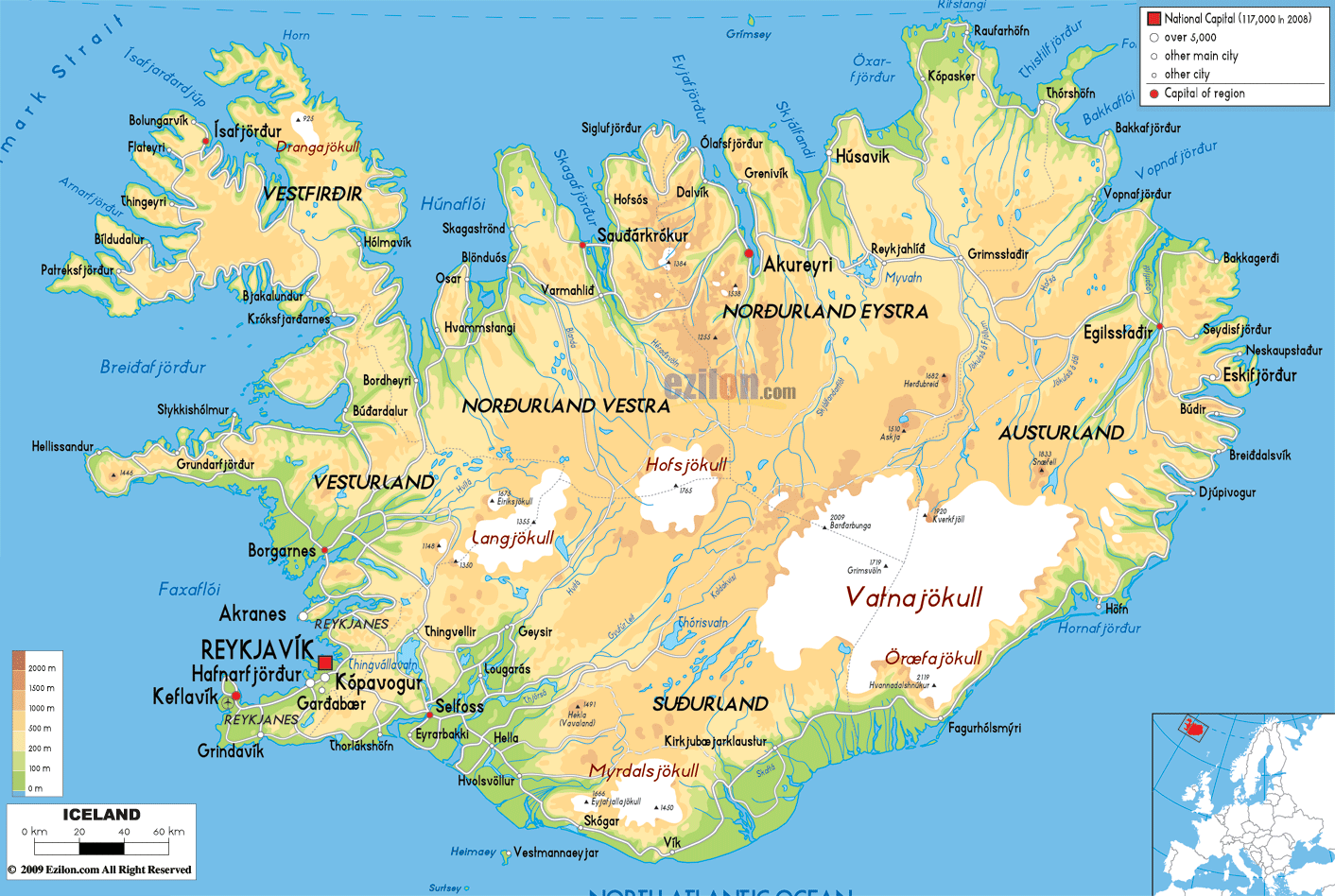
Iceland, the land of fireplace and ice, holds a novel place on the European map. Its remoted location, dramatic landscapes, and geological dynamism make it a captivating topic for geographical examine. This text delves into the island’s cartographic illustration, exploring its location, bodily options, and the way maps reveal its distinctive character. We’ll transfer past a easy visible illustration to look at how totally different map varieties illuminate totally different elements of Iceland’s geography, from its volcanic exercise to its glacial formations, its human settlements to its distinctive ecosystem.
Iceland’s Place: A North Atlantic Outpost
A look at any world map immediately reveals Iceland’s distant location. Located within the North Atlantic Ocean, it sits astride the Mid-Atlantic Ridge, a tectonic plate boundary the place the North American and Eurasian plates meet. This geological setting is prime to understanding Iceland’s volcanic exercise and its attribute landscapes. Maps showcasing tectonic plates vividly illustrate Iceland’s place at this significant juncture, highlighting its significance within the world geological context. Its proximity to Greenland and the Faroe Islands, as depicted on regional maps, additional emphasizes its remoted place, but its connection to a broader North Atlantic ecosystem. The space from continental Europe, clearly proven on numerous map projections, explains its relative isolation all through historical past and its distinctive cultural improvement.
Bodily Geography: Hearth and Ice on the Map
Iceland’s bodily geography is very various, a testomony to its volcanic origins and glacial historical past. Topographic maps are essential instruments for understanding this range. These maps, with their contour traces and elevation shading, reveal the dramatic interaction of mountains, glaciers, and lowlands. The huge ice caps, like Vatnajökull and Langjökull, dominate the highlands, their extent clearly seen on even small-scale maps. These maps additionally spotlight the quite a few volcanoes, each lively and dormant, scattered throughout the island, a lot of that are located alongside the Mid-Atlantic Ridge. The distribution of those options, as proven on thematic maps specializing in geology or volcanic exercise, underscores the island’s dynamic geological processes.
Moreover, maps can reveal the intricate community of rivers and glacial rivers that carve their method by means of the panorama. These waterways, usually originating from glacial meltwater, play a significant function in shaping the island’s ecology and influencing its human settlements. Hydrological maps, depicting river programs and water our bodies, present helpful insights into Iceland’s water assets and their distribution. The coastal areas, proven intimately on larger-scale maps, are characterised by fjords – lengthy, slender inlets – a testomony to glacial erosion. These fjords, essential for fishing and transportation all through Icelandic historical past, are outstanding options on any map of the island.
Human Geography: Settlement Patterns and Infrastructure
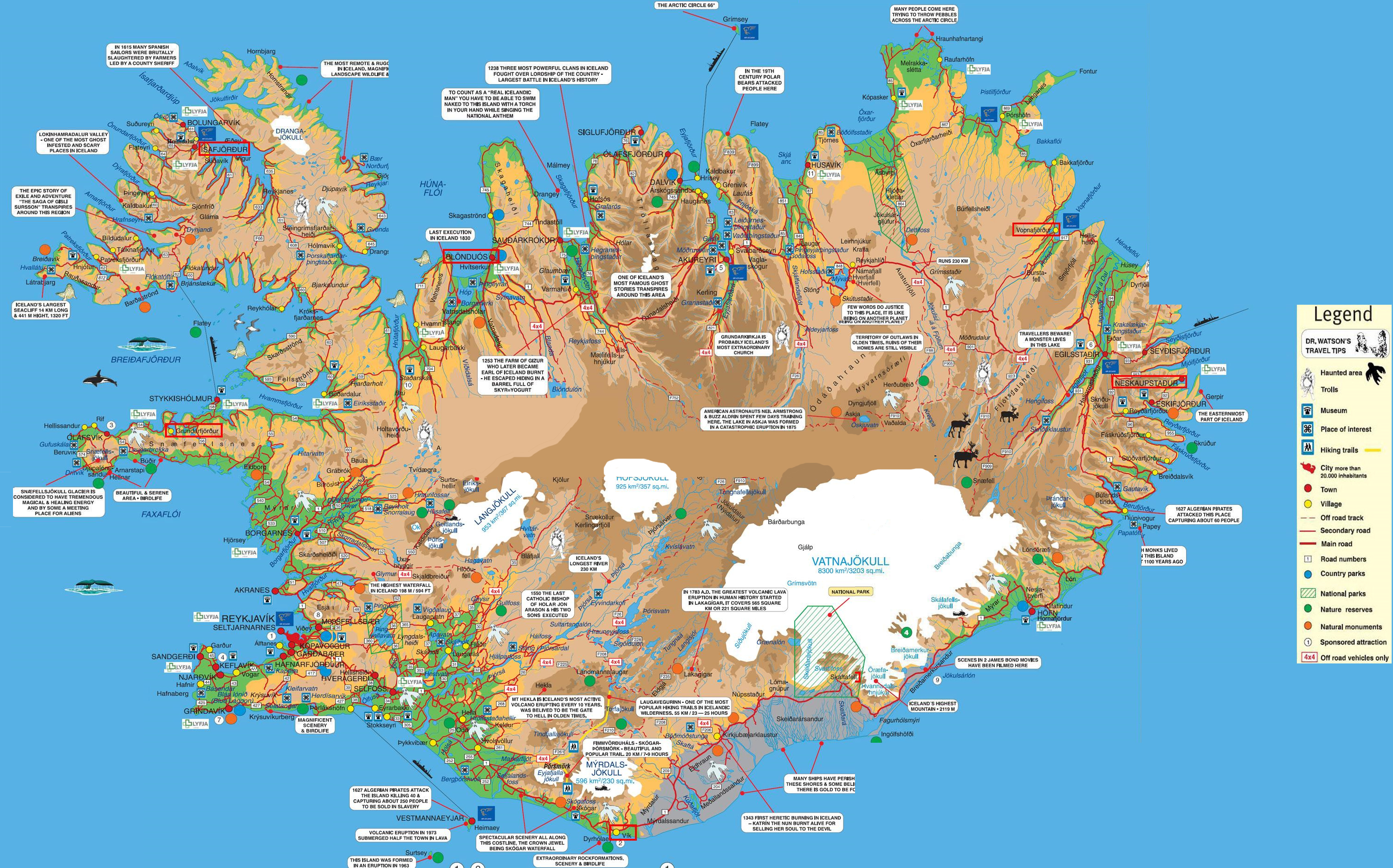
Maps additionally illuminate the human imprint on the Icelandic panorama. Inhabitants density maps clearly present the focus of settlements alongside the coastal areas, significantly within the southwest, reflecting the affect of local weather and accessibility. The sparse inhabitants within the highlands is a direct consequence of the tough surroundings. Street networks, depicted on highway maps, reveal the challenges of traversing the island, with many areas solely accessible throughout sure occasions of the yr. The restricted highway infrastructure within the highlands contrasts sharply with the well-developed highway system within the extra populated coastal areas.
Historic maps present a captivating glimpse into the evolution of human settlement in Iceland. These maps, usually exhibiting the places of early farms and settlements, illustrate the gradual growth of human exercise throughout the island over centuries. In addition they reveal the affect of historic occasions, comparable to volcanic eruptions and adjustments in local weather, on settlement patterns. Evaluating historic and modern maps highlights the numerous adjustments in inhabitants distribution and infrastructure improvement over time.
Ecosystem Mapping: Biodiversity in a Distinctive Surroundings
Iceland’s distinctive ecosystem is one other side that may be successfully illustrated by means of mapping. Vegetation maps spotlight the distribution of various plant communities, reflecting the affect of altitude, local weather, and volcanic exercise. The restricted biodiversity, in comparison with different areas of Europe, is clearly evident. Maps depicting the distribution of key animal species, such because the Arctic fox and numerous seabirds, illustrate the island’s distinctive fauna. The intricate relationship between the bodily surroundings and the organic communities is clearly demonstrated by means of the overlay of various thematic maps.
Marine maps are important for understanding Iceland’s wealthy marine surroundings. These maps depict the extent of the continental shelf, the distribution of fishing grounds, and the placement of vital marine habitats. Iceland’s important fishing trade, a cornerstone of its financial system, is immediately linked to the assets depicted on these maps. The mapping of ocean currents additionally highlights the island’s function as a crossroads for numerous marine species and its affect on the native local weather.
Map Projections and Their Impression on Iceland’s Illustration
The selection of map projection considerably impacts how Iceland is depicted. Whereas cylindrical projections, such because the Mercator projection, are generally used, they distort the form and dimension of Iceland, significantly at larger latitudes. Equidistant projections provide a extra correct illustration of distances, whereas equal-area projections protect the relative sizes of landmasses. The number of an applicable projection is essential for precisely representing Iceland’s geographical options and guaranteeing a devoted depiction of its dimension and form relative to different landmasses.
Conclusion: Maps as Instruments for Understanding Iceland
Iceland’s geography is exceptionally various and dynamic. Maps, of their numerous kinds, are indispensable instruments for understanding this complexity. From showcasing the island’s geological origins and its dramatic landscapes to illustrating human settlement patterns and the distinctive ecosystem, maps present a vital visible illustration of Iceland’s character. By inspecting totally different map varieties and projections, we are able to achieve a deeper appreciation for the intricate interaction of geological forces, weather conditions, and human actions which have formed this outstanding island nation. The examine of Iceland by means of maps isn’t merely a visible train; it is a journey into the guts of a geographically fascinating and distinctive a part of Europe. The extra we look at these maps, the extra we recognize the intricate story they inform of Iceland’s formation, evolution, and place inside the broader context of the North Atlantic and Europe.






Closure
Thus, we hope this text has offered helpful insights into Iceland: A Geographic Exploration By Maps. We thanks for taking the time to learn this text. See you in our subsequent article!