Mapping the World: A Journey By Cartography’s Historical past, Methods, and Future
Associated Articles: Mapping the World: A Journey By Cartography’s Historical past, Methods, and Future
Introduction
With enthusiasm, let’s navigate by way of the intriguing matter associated to Mapping the World: A Journey By Cartography’s Historical past, Methods, and Future. Let’s weave fascinating data and supply recent views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Mapping the World: A Journey By Cartography’s Historical past, Methods, and Future

Maps. Seemingly easy representations of the world, they’re in actuality complicated artifacts reflecting not solely geography but in addition the cultural, technological, and political landscapes of their creators. From historic cave work depicting looking grounds to stylish digital globes accessible on smartphones, maps have been essential instruments for navigation, exploration, planning, and understanding our place within the vastness of the Earth. This text delves into the multifaceted world of maps, exploring their historical past, the varied methods employed of their creation, and the thrilling developments shaping their future.
A Historic Perspective: From Cave Work to World Positioning Techniques
The earliest types of mapping could be traced again to prehistoric cave work, rudimentary depictions of terrain and looking routes. These weren’t maps within the fashionable sense, however they characterize a elementary human want to grasp and document spatial relationships. Historical civilizations just like the Babylonians, Egyptians, and Greeks additional developed cartography. Babylonian clay tablets relationship again to the seventh century BC depict land divisions and irrigation methods, demonstrating a sensible utility of mapping for administrative functions. The Egyptians utilized maps for surveying and land administration, essential for his or her intricate agricultural system alongside the Nile.
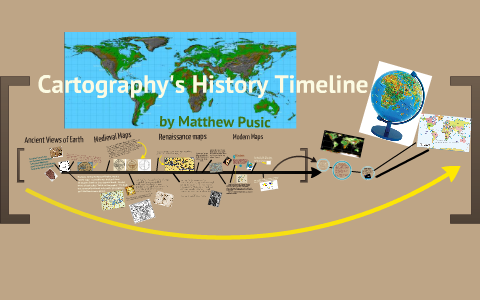
Greek cartography, nonetheless, marked a big leap ahead. Anaximander (sixth century BC) is credited with creating one of many earliest identified world maps, a flat disc surrounded by ocean. Whereas inaccurate by fashionable requirements, his work demonstrated an important shift in the direction of a extra systematic and theoretical strategy to mapping. Later, Ptolemy (2nd century AD) produced a extremely influential atlas, Geographia, which integrated geographical coordinates and standardized map projections, turning into a benchmark for hundreds of years. His work, although containing inaccuracies as a result of restricted exploration, established a framework that guided mapmaking for over a millennium.
The medieval interval noticed a decline within the high quality and class of mapmaking in Europe, with the prevalence of T-O maps – symbolic representations putting Jerusalem on the heart of a round world divided by the Mediterranean Sea and the rivers Nile and Euphrates. These maps mirrored a geocentric worldview and a give attention to non secular and symbolic that means reasonably than correct geographical illustration. Nevertheless, alongside these symbolic maps, extra sensible portolan charts emerged, utilized by sailors for navigation. These charts, meticulously detailed with compass rose and coastal options, have been essential for maritime exploration and commerce.
The Age of Exploration, starting within the fifteenth century, revolutionized cartography. The voyages of discovery led to the buildup of latest geographical information, demanding extra correct and detailed maps. Cartographers like Gerardus Mercator developed progressive map projections, notably the Mercator projection, which, whereas distorting landmasses at increased latitudes, tremendously aided navigation by preserving rhumb traces (traces of fixed bearing). The next centuries witnessed a flourishing of cartography, fueled by scientific developments and the event of surveying methods.
Methods and Applied sciences in Mapmaking
The creation of a map entails a fancy interaction of surveying, information acquisition, projection, and visualization. Conventional strategies relied on meticulous floor surveys, utilizing devices like theodolites and airplane tables to measure distances and angles. This painstaking course of, typically requiring in depth fieldwork, yielded extremely correct information for smaller-scale maps. Aerial pictures and satellite tv for pc imagery revolutionized mapmaking within the twentieth century, offering huge quantities of information overlaying massive areas. These applied sciences allowed for the creation of extra complete and detailed maps, notably for distant or inaccessible areas.
Map projections are essential for remodeling the three-dimensional Earth onto a two-dimensional floor. No projection can completely characterize the Earth’s curvature with out distortion; every projection entails trade-offs, emphasizing sure properties like space, form, or distance whereas compromising others. Frequent projections embody the Mercator projection (used for navigation), the Lambert conformal conic projection (used for aeronautical charts), and the Albers equal-area conic projection (used for thematic mapping).
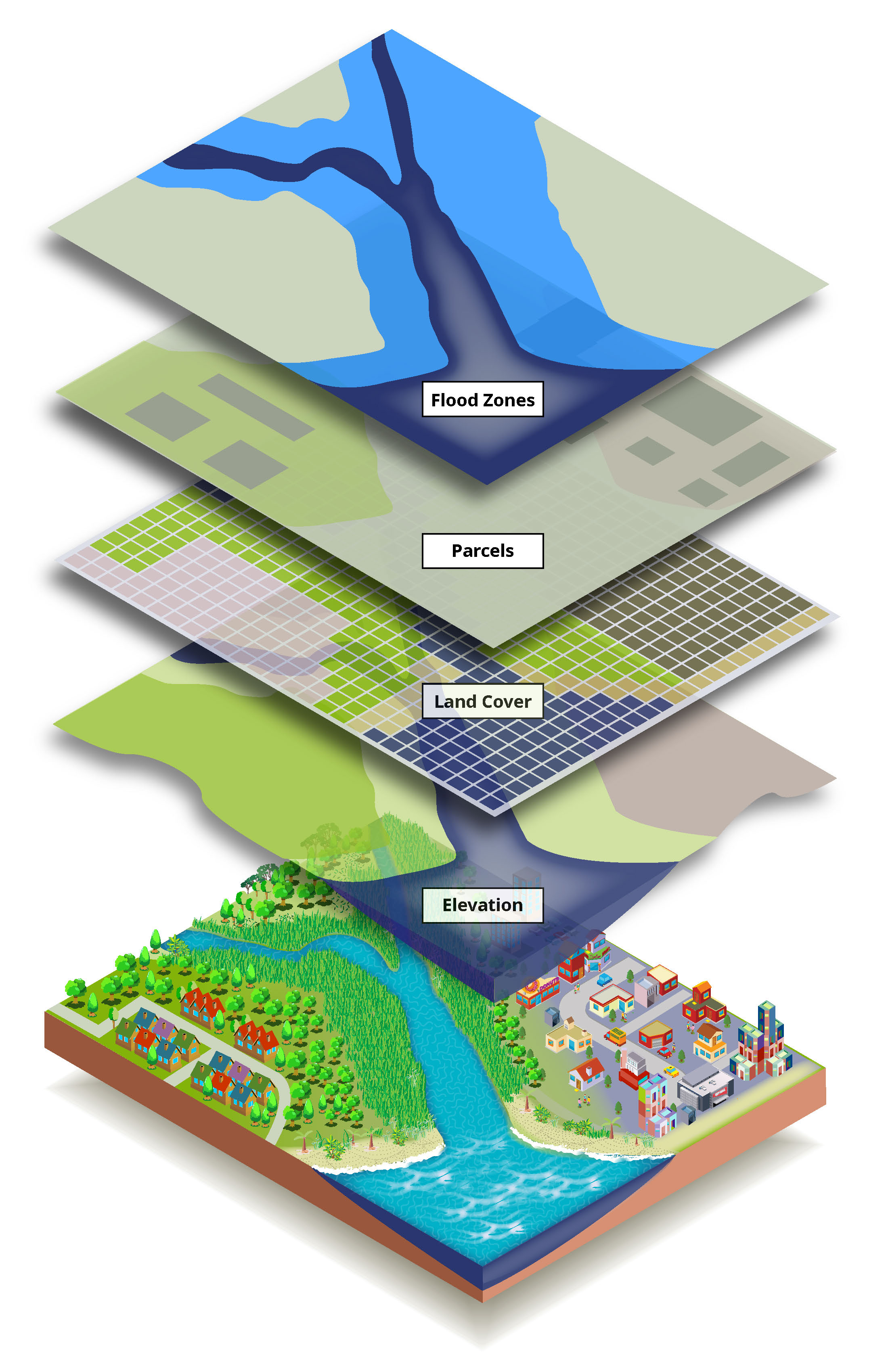
The event of Geographic Data Techniques (GIS) additional reworked mapmaking. GIS are computer-based methods that permit for the storage, manipulation, evaluation, and visualization of geographical information. GIS combine various information sources, similar to satellite tv for pc imagery, aerial images, census information, and topographical surveys, enabling the creation of extremely subtle and interactive maps. GIS purposes vary from city planning and environmental monitoring to catastrophe response and useful resource administration.
Varieties of Maps and Their Functions
The variety of maps displays the wide selection of purposes they serve. Topographic maps illustrate the Earth’s floor options, together with elevation, terrain, and water our bodies. These maps are important for planning infrastructure initiatives, navigation, and environmental research. Thematic maps give attention to particular themes, similar to inhabitants density, local weather patterns, or illness distribution. These maps are beneficial instruments for analyzing spatial patterns and understanding geographical phenomena. Navigation maps, designed for guiding vacationers, prioritize routes and landmarks. Street maps, nautical charts, and aeronautical charts are all examples of navigation maps tailor-made to completely different modes of transportation.
Cadastral maps depict land possession and limits, essential for property administration and authorized functions. Geological maps illustrate the distribution of rocks and minerals, offering important data for useful resource exploration and geological research. Political maps depict nations, states, and different administrative divisions, highlighting political boundaries and offering a framework for understanding geopolitical relationships. Historic maps supply insights into previous geographical configurations and human settlements, contributing to historic analysis and concrete planning.
The Way forward for Mapping
The way forward for mapmaking is marked by steady technological developments and increasing purposes. The growing availability of high-resolution satellite tv for pc imagery and crowdsourced information is resulting in extra detailed and dynamic maps. Digital actuality (VR) and augmented actuality (AR) applied sciences are remodeling how we work together with maps, providing immersive experiences and enhanced visualization capabilities. The mixing of synthetic intelligence (AI) is automating many features of mapmaking, from information processing and evaluation to the technology of map options. AI-powered methods can establish patterns, predict tendencies, and enhance the accuracy and effectivity of map creation.
Moreover, the event of 3D mapping applied sciences is offering extra complete representations of the Earth’s floor, together with constructing fashions and subterranean options. These 3D maps are beneficial for city planning, infrastructure administration, and catastrophe response. The growing accessibility of mapping applied sciences is empowering people and communities to create and share their very own maps, fostering citizen engagement and participatory mapping initiatives. OpenStreetMap, a collaborative mission to create a free editable map of the world, exemplifies this development.
In conclusion, maps are excess of easy visible representations of the world; they’re highly effective instruments reflecting human data, ingenuity, and understanding of our planet. From their humble beginnings in cave work to their subtle digital types, maps have performed, and proceed to play, a significant position in navigation, exploration, planning, and understanding our world. As expertise continues to advance, the way forward for mapping guarantees much more correct, detailed, and interactive maps, providing unprecedented insights into our planet and its complexities.





Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied beneficial insights into Mapping the World: A Journey By Cartography’s Historical past, Methods, and Future. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!