Navigating the Branches of Life: A Complete Information to Creating and Decoding an Evolution Idea Map
Associated Articles: Navigating the Branches of Life: A Complete Information to Creating and Decoding an Evolution Idea Map
Introduction
With nice pleasure, we’ll discover the intriguing matter associated to Navigating the Branches of Life: A Complete Information to Creating and Decoding an Evolution Idea Map. Let’s weave fascinating info and provide contemporary views to the readers.
Desk of Content material
Navigating the Branches of Life: A Complete Information to Creating and Decoding an Evolution Idea Map

Evolution, the cornerstone of recent biology, is a posh and multifaceted idea. Understanding its intricacies requires not solely absorbing an enormous quantity of data but additionally greedy the interconnectedness of varied ideas and processes. A strong instrument for attaining that is the idea map. This text explores the creation and interpretation of a complete evolution idea map, detailing key ideas, their relationships, and potential purposes.
I. Core Ideas for an Evolution Idea Map:
A strong evolution idea map must embody a variety of interconnected concepts. These could be broadly categorized as follows:
A. The Mechanisms of Evolution:
-
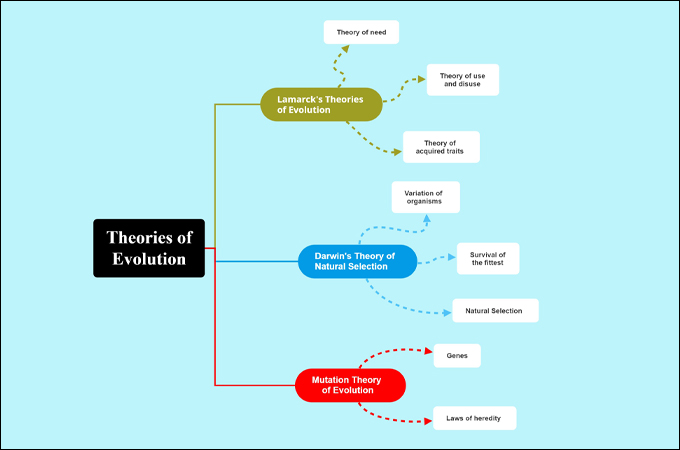
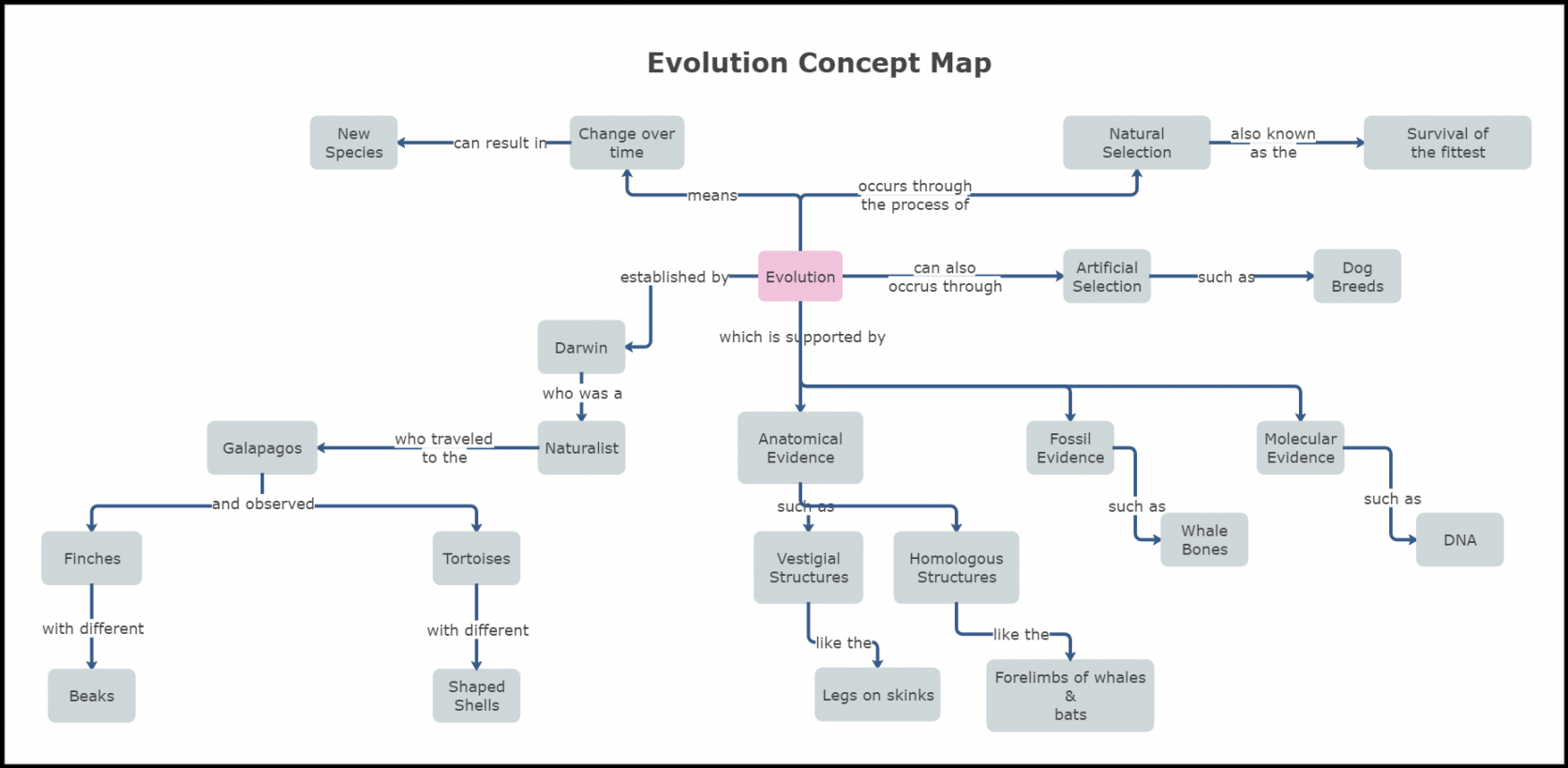
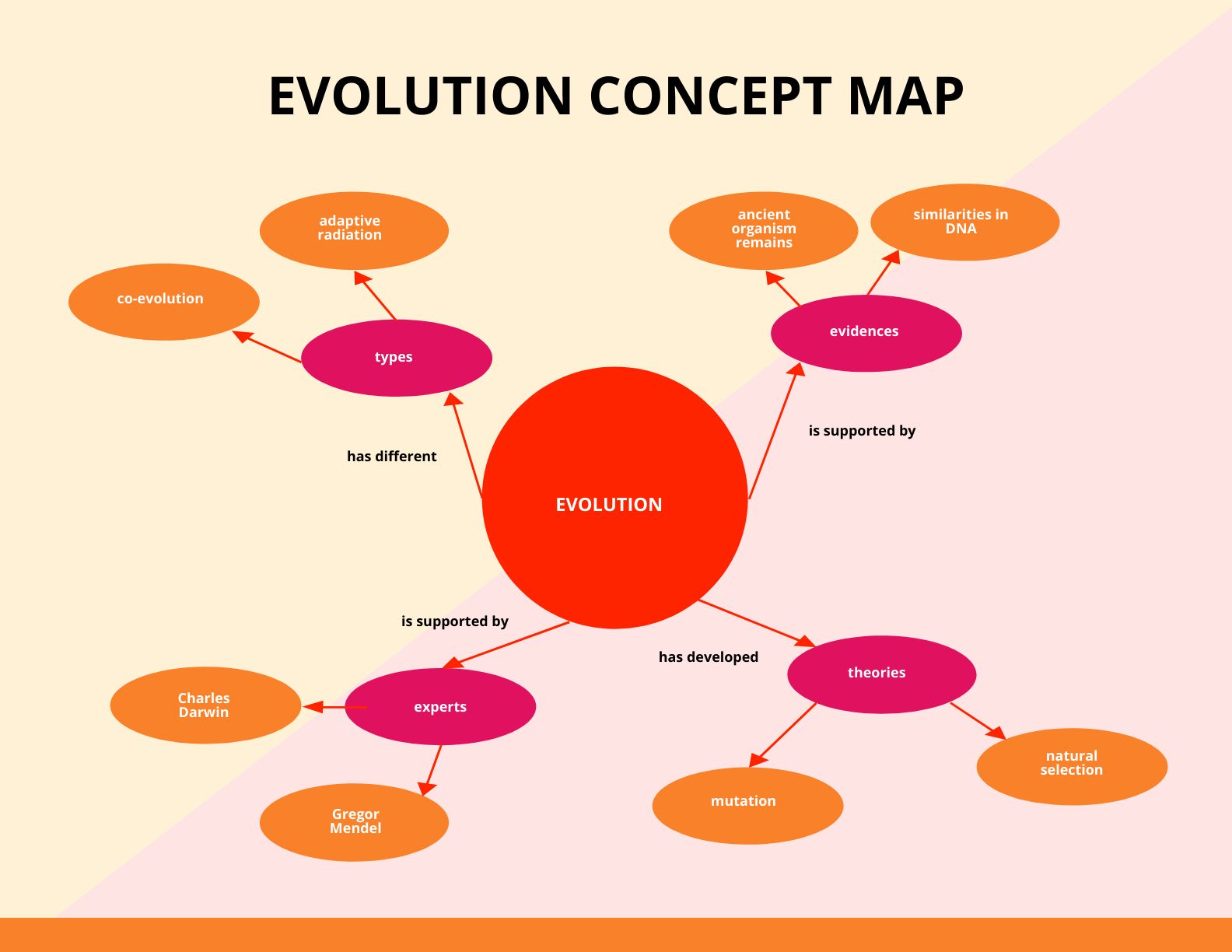
Pure Choice: That is arguably probably the most essential idea. The map ought to clearly outline pure choice because the differential survival and copy of people primarily based on heritable traits. Join this to ideas like variation, inheritance, and health.
-
Genetic Drift: This random fluctuation of gene frequencies, notably important in small populations, must be contrasted with pure choice. Spotlight its position in altering allele frequencies regardless of their adaptive worth. Sub-concepts like founder impact and bottleneck impact could be included.
-
Gene Move: This idea describes the motion of genes between populations. Illustrate how gene movement can enhance genetic variation inside a inhabitants and scale back variations between populations.
-
Mutation: That is the final word supply of genetic variation. Present its position in introducing new alleles right into a inhabitants, offering the uncooked materials upon which pure choice acts. Differentiate between several types of mutations (level mutations, chromosomal mutations).
-
Sexual Choice: This particular type of pure choice focuses on traits that improve mating success. Join it to ideas like sexual dimorphism and intrasexual/intersexual choice.
B. Proof for Evolution:
-
Fossil Report: This offers direct proof of previous life and the transitions between species. Illustrate how the fossil document paperwork the extinction of species and the emergence of latest ones. Embody ideas like transitional fossils and relationship methods.
-
Comparative Anatomy: This includes evaluating the anatomical buildings of various species. Spotlight homologous buildings (shared ancestry) and analogous buildings (convergent evolution). Embody vestigial buildings as proof of evolutionary historical past.
-
Comparative Embryology: This focuses on the similarities in embryonic growth throughout totally different species. Illustrate how similarities in early growth mirror shared ancestry.
-
Molecular Biology: This offers compelling proof by way of DNA and protein sequence comparisons. Present how phylogenetic bushes constructed utilizing molecular information help evolutionary relationships. Embody ideas like molecular clocks and conserved genes.
-
Biogeography: The geographic distribution of species offers insights into evolutionary historical past. Illustrate how the distribution of species on totally different continents displays continental drift and different historic occasions.
C. Outcomes of Evolution:
-
Adaptation: That is the method by which organisms develop into higher suited to their surroundings. Join this to pure choice and the particular traits that improve survival and copy.
-
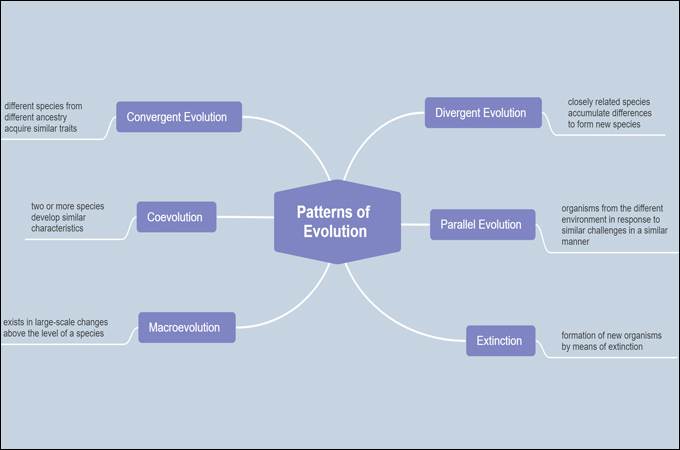
Speciation: That is the method by which new species come up. Illustrate the totally different modes of speciation (allopatric, sympatric, parapatric). Embody ideas like reproductive isolation and reproductive boundaries.
-
Extinction: That is the disappearance of species. Join it to environmental adjustments, competitors, and different elements that may result in the demise of a species. Illustrate the position of mass extinctions in shaping the historical past of life.
-
Coevolution: This describes the reciprocal evolutionary adjustments between interacting species. Illustrate examples like predator-prey relationships and plant-pollinator interactions.
-
Phylogenetic Bushes: These diagrams symbolize the evolutionary relationships between species. Clarify how phylogenetic bushes are constructed and interpreted, highlighting ideas like clades and customary ancestors.
II. Establishing the Idea Map:
Making a complete evolution idea map requires a scientific method:
-
Determine Central Ideas: Start by figuring out the core ideas listed above. These will kind the central nodes of your map.
-
Set up Relationships: Decide the relationships between the core ideas. Use linking phrases and phrases to explain these relationships (e.g., "results in," "leads to," "is brought on by," "is an instance of").
-
Use Hierarchical Construction: Set up the ideas hierarchically, with broader ideas on the prime and extra particular ideas branching down.
-
Visible Illustration: Use a visible illustration like circles, containers, or different shapes to symbolize the ideas. Join them with strains to indicate the relationships.
-
Cross-Linking: Do not hesitate to cross-link ideas from totally different classes. For instance, join "pure choice" to "adaptation" and "speciation."
-
Use Shade-Coding: Use totally different colours to symbolize totally different classes of ideas, making the map simpler to navigate.
-
Iteration and Refinement: The creation of an idea map is an iterative course of. Evaluation and refine your map as you study extra about evolution.
III. Decoding the Idea Map:
A well-constructed idea map serves as a strong instrument for understanding and recalling info. By visually representing the interconnectedness of ideas, it facilitates deeper comprehension. Decoding the map includes:
-
Tracing Relationships: Comply with the hyperlinks between ideas to know how they relate to 1 one other. Determine cause-and-effect relationships and suggestions loops.
-
Figuring out Key Connections: Give attention to the central ideas and their most essential connections. These symbolize the elemental ideas of evolution.
-
Understanding the Hierarchy: Analyze the hierarchical construction to understand the relative significance and specificity of various ideas.
-
Figuring out Gaps in Understanding: If there are areas the place you battle to know the connections between ideas, it highlights areas requiring additional examine.
-
Utilizing the Map for Research and Evaluation: The idea map can be utilized as a examine support for exams or shows. It offers a structured overview of the fabric and facilitates recall.
IV. Purposes of the Evolution Idea Map:
The purposes of an evolution idea map prolong past private examine:
-
Academic Software: Idea maps can be utilized as efficient educating instruments in lecture rooms, serving to college students visualize and perceive the advanced relationships inside evolutionary biology.
-
Analysis Software: They can be utilized to arrange and synthesize analysis findings, facilitating the identification of gaps in data and the formulation of latest analysis questions.
-
Communication Software: Idea maps can be utilized to speak advanced concepts clearly and concisely to a wider viewers.
-
Downside-Fixing Software: By visualizing the interconnectedness of ideas, idea maps can support in problem-solving associated to evolutionary questions.
In conclusion, a complete evolution idea map is a precious instrument for understanding and speaking the intricacies of this basic organic precept. By systematically organizing and visually representing key ideas and their relationships, it facilitates deeper studying, enhances reminiscence retention, and offers a framework for additional exploration and analysis. The creation and interpretation of such a map are usually not merely workout routines in group; they’re energetic studying methods that contribute considerably to a strong understanding of the processes which have formed life on Earth.




Closure
Thus, we hope this text has supplied precious insights into Navigating the Branches of Life: A Complete Information to Creating and Decoding an Evolution Idea Map. We respect your consideration to our article. See you in our subsequent article!